Target Pests
|
Fungus gnat larvae - Bradysia spp.- in potting mixes.
Black vine weevil - Otiorhynchus sulcatus - in potted plants e.g. cyclamen, maiden hair fern, polyanthus, fuchsia, strawberry, raspberry, rhododendron, azalea, yews, conifers, walnuts, begonias, impatiens and geraniums.
African Black Beetle - Heteronychus arator - in turf.
Sirex Wasp control for Forestry
Available Mid May to Mid August
|
 |
 |
|
Description
|
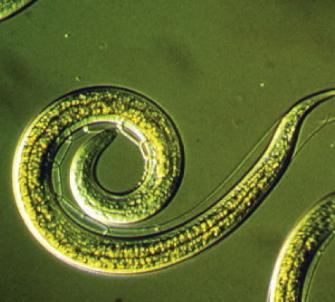
ENs are microscopic, simple round worms, colourless, unsegmented and lacking appendages.
Nematodes as a group, may be free - living, predaceous or parasitic. Many of the parasitic species cause important diseases of plants, animals and humans.
Entomopathogenic or insecticidal nematodes are beneficial in attacking insect pests, which they are lethal parasites. They kill insects by entering them and releasing a bacterium that multiplies within the insect. ENs are very different from PPNs (Plant Parasitic Nematodes) i.e. plant pests.
|
 |
 |
| |
The bacterium, harmless to humans and other animals, serves as a food source for the nematode. The nematodes hone in on the larva's carbon dioxide exhalations, travelling in the thin film of moisture that surrounds the particles of the medium.
After approximately 14 days the nematodes have reproduced inside the victim and the larval cadaver ruptures and releases up to 10,000 x the number of ENs that had originally infected and these go in search of new prey.
|
 |
 |

|
Detailed descriptions and instructions for use are provided in
The Good Bug Book - Second Edition Available from good bug suppliers
Or view or download a PDF file of the Book entry for Nematodes.
|
 |
 |

Sirex wasp a pest in forestry
|









